How do Doctors Know it’s FTD?
Dr. Chen, our dad’s neurologist, sent home some pictures of what our dad’s brain looks like. The pictures show that the front of Dad’s brain is smaller than it should be. The disease makes the cells stop working and the brain gets smaller. We looked at the pictures, but it was still confusing. Mom arranged for us to meet with Dr. Chen and he showed us a model of the brain. We asked questions and learned a lot and then the pictures of Dad’s brain made more sense.
It is not easy for doctors to know if a person has FTD. A person may need to see many different doctors to find out what is wrong. When a family doctor thinks it may be a problem with the brain, he or she sends the person to a special doctor who is an expert in how the brain works. This doctor is called a .
The neurologist asks lots of questions about what changes the person and their family have noticed. The doctor does a full check-up and uses special tests to measure how well the brain is working. The tests include long paper and pencil tests (kind of like the ones you take in school), blood work, and taking special pictures of the person’s brain. It can take many visits to do all the tests but the tests do not hurt.
Some of the tests use technology to look at the brain. It’s like having x-ray vision to look inside the body at a broken bone, only the brain is more complicated. There are different types of brain pictures or scans:
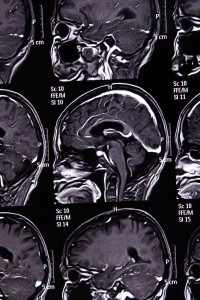
The picture below is called an . The letters stand for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. It can show the size, shape and thickness of brain tissue. Doctors can see if the structure of the brain looks the same or different from pictures of a normal, healthy brain.
This MRI shows several different pictures of a person’s head from the side, with the mouth and nose facing left. The picture in the middle shows the brain in gray, just inside the thin white outline of the skull.
Another type of scan doctors use is called a . P-E-T stands for Positron Emission Tomography. It allows the doctor to see how active different parts of the brain are when the person is thinking. The pattern of areas that are more active and less active can help the doctor know if the person has FTD.
Once the tests are complete, doctors gather information together to make a . The diagnosis is the name given to a person’s illness.